@markdown
# XOR 문제 Deep Learning 하기
____
- XOR 문제는 계산으로는 쉽게 풀리지만, Neural Network으로 학습하여 해결하기엔 어려운 문제
- 하나의 unit(logistic regression)으로는 절대로 해결할 수 없던 문제였다.
- 해결 방법으로 여러 개의 unit(logistic regression)을 연결하여 구성된 Neural Network으로 XOR 문제를 해결했다.
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">K = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1)+b1)
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(K, W2)+b2)
하나만 이용됐던 sigmoid 함수를 다음 sigmoid의 입력값으로 넣어 Neural Network를 구성하는 방법이다.
</code></pre>
## Neural Network - XOR
____
- XOR 문제를 Neural Network를 구성하여 해결한다.
- Logistic Regression으로는 해결할 수 없지만, 여러개의 Logistic을 연결하여 해결 할 수 있다.
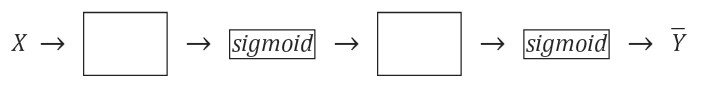
### Logistic Regression으로 XOR 문제 학습하기
- sigmoid 함수 하나만으로 학습시킨 모델로 예측결과의 정확도가 50%밖에 되지 않는다.
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px"># Logistic Regression 사용한 XOR 문제 해결
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
learning_rate = 0.1
x_data = [[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]]
y_data = [[0],
[1],
[1],
[0]]
x_data = np.array(x_data, dtype=np.float32)
y_data = np.array(y_data, dtype=np.float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 2])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W) + b)
cost = -tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(10001):
sess.run(train, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, sess.run(cost, feed_dict={
X: x_data, Y: y_data}), sess.run(W))
h, c, a = sess.run([hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print("\nHypothesis: ", h, "\nCorrect: ", c, "\nAccuracy: ", a)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">로지스틱 회귀 학습결과 XOR 문제를 해결할 수 없다.
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.90373993]
[ 0.7384038 ]
[ 0.85757399]
[ 0.6441645 ]]
Correct:
[[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]]
Accuracy: 0.5
정확도가 0.5로 예측값이 틀렸다.
</code></pre>
<br/>
### Neural Network - Layer 2개로 XOR 문제 학습하기
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
learning_rate = 0.1
x_data = [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]
y_data = [[0], [1], [1], [0]]
x_data = np.array(x_data, dtype=np.float32)
y_data = np.array(y_data, dtype=np.float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 2])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2]), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2]), name='bias1')
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1]), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias2')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
cost = -tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(10001):
sess.run(train, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data}), sess.run(W))
h, c, a = sess.run([hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print("\nHypothesis: \n", h, "\nCorrect: \n", c, "\nAccuracy: \n", a)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">Logistic Unit 2개 연결한 Neural Network 실행결과
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.01131542]
[ 0.98489004]
[ 0.98962176]
[ 0.00958671]]
Correct:
[[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy:
1.0
</code></pre>
<br/>
## Wide Neural Network
- 입력값을 Wide 하게 feed한 Network로 기존의 [2, 2]에서 [2, 10]으로 넓혔다.
### 입력값 2개 Neural Network
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2]), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2]), name='bias1')
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1]), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias2')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">입력값이 2개일 경우 실행결과
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.01854506]
[ 0.98510611]
[ 0.98632425]
[ 0.01610798]]
Correct:
[[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy: 1.0
</code></pre>
<br/>
### 입력값 10개 Neural Network
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 10]), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]), name='bias1')
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1]), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias2')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">입력값이 10개일 경우 실행결과
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.0060874 ]
[ 0.99390703]
[ 0.99216485]
[ 0.00812306]]
Correct: [[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy: 1.0
Wide한 Neural Network의 경우 예측값이 좀 더 정확한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
</code></pre>
<br/>
## Deep-Wide Neural Network
____
- Layer 갯수 별 cost 비교 하기 실행결과 첨부
- Neural Net을 넓고, 깊게 설계하면 앞의 학습 모델 보다 더 작고, 0에 보다 더 가까운 cost와 정확한 예측값을 얻을 수 있다.
- hypothesis의 계산 방식 Layer1의 결과를 Layer2에, Layer2의 결과를 Layer3에 전달하고, Layer3를 hypothesis에 전달하는 방식이다.
- Layer를 쌓을 수록 신경망이 Deep 해지는 것이다.
### 2단 Layer로 구성된 Deep Neural Network
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
learning_rate = 0.1
x_data = [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]
y_data = [[0], [1], [1], [0]]
x_data = np.array(x_data, dtype=np.float32)
y_data = np.array(y_data, dtype=np.float32)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 2])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2]), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2]), name='bias1')
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1]), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias2')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
cost = -tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(10001):
sess.run(train, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data}), sess.run(W))
h, c, a = sess.run([hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print("\nHypothesis: \n", h, "\nCorrect: \n", c, "\nAccuracy: \n", a)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">2단 Layer Deep Neural Network 실행결과
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.16991137]
[ 0.88076794]
[ 0.74543869]
[ 0.12266544]]
Correct:
[[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy:
1.0
</code></pre>
<br/>
### 4단 Layer로 구성된 Deep Neural Network
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 10]), name='weight1')
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]), name='bias1')
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 10]), name='weight2')
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]), name='bias2')
layer2 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
W3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 10]), name='weight3')
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]), name='bias3')
layer3 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer2, W3) + b3)
W4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1]), name='weight4')
b4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias4')
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer3, W4) + b4)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">4단 Deep-Wide Neural Network 실행결과
10000 0.00308841 [[-2.90717649]
[-0.96270812]]
Hypothesis:
[[ 0.0031194 ]
[ 0.99797934]
[ 0.9959138 ]
[ 0.00310728]]
Correct:
[[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]]
Accuracy:
1.0
2단과 4단 Layer로 각각 학습된 모델의 예측값을 비교한 결과 4단 Layer로 예측한 값이 더 정확한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
</code></pre>
<br/>
> 소스코드 - 모두를 위한 머신러닝 김석훈 교수님 강의 참고 : ([https://hunkim.github.io/ml/](https://hunkim.github.io/ml/))
'Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TensorFlow - MNIST ReLU, Xavier 초기화, Dropout 적용하여 정확도 높이기 (0) | 2017.08.15 |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow - MNIST 데이터 셋 활용한 손 글씨 인식 모델 구현 (0) | 2017.08.07 |
| TensorFlow - Learning Rate, Data Preprocessing, Overfitting (0) | 2017.08.01 |
| TensorFlow - Softmax Regression(2) (0) | 2017.07.13 |
| TensorFlow - Softmax Regression(1) (0) | 2017.07.12 |