@markdown
# TensorFlow Learning Rate, Data Preprocessing, Overfitting
<br/>
## Learning Rate
____
- Gradient Descent 알고리즘의 cost 값(최소값)을 찾아가는 과정에서 다음 step의 point를 얼마나 움직일지 결정하는 것
- 여러번 학습한 후 결과에 따라 적절한 learning rate을 정하는 것이 중요하다.
- learning rate가 크면 overshooting 발생
- overshooting : 경사면에 step이 너무 크다면 학습이 이루어지지 않을 것이고, cost 값이 숫자가 아닌 값이 나타난다.
- 너무 작은 learning rate을 지정하면 step이 조금씩 진행이 되면서 곡선의 최저점 즉 cost값을 구하기 전에 학습이 끝난다.
- 보통 0.01로 시작하여 cost 값을 확인하며 적절한 learning rate를 정해준다.
## Data Preprocessing(데이터 선처리)
____
- 경사하강법의 최저점을 구하기 위해서, x 데이터를 선처리 해야할 경우가 있다.
- 데이터 간 차이가 클 경우, Normalization을 해준다.
- 표준화 방법을 통해 데이터 정규화를 시켜준다.
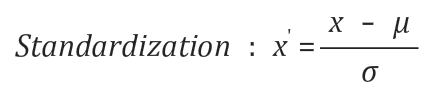
## Overfitting
____
- 학습 데이터에 치중된 모델이 만들어질 경우, 실제 예측을 위한 데이터가 주어졌을 때 정확도가 떨어질 수가 있다.
방지 하기 위해서
1. training data가 많이 가질수록 좋다.
2. features의 갯수를 줄이는 것
3. 기술적으로 Regularization(일반화) 시킨다.
- 기존의 Cost 함수 뒤에 일반화 시키는 식을 추가해 프로그램 작성을 한다.
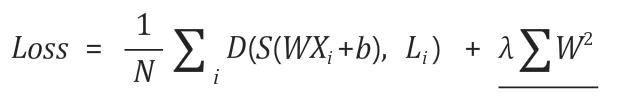
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">l2reg = 0.001 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(W))
</code></pre>
<br/>
## Machine Learning 모델 평가
____
- 초기의 데이터셋을 학습 데이터 셋 + 모의 데이터 셋 + 테스트 데이터 셋으로 구분지어 학습을 시킨다.
1. 완벽한 Traning data set으로 학습시킨다.
2. Validation data set을 가지고 모델의 상수(learning rate, 람다 값 등)들이 어떤 값이 좋을지 튜닝해 결정한다.
3. 학습이 끝나면 Testing data set으로 모델이 잘 동작하는지 확인한다.
## Online Learning
____
- Training set 데이터를 일정 크기로 잘라 학습을 시키는 방법이다.
- 추가적으로 학습시킬 데이터가 발생할 경우 전체 데이터 셋에 포함시키지 않고, 기존의 학습된 모델에 학습하는 방법이다.
## Learning Rate 조절 실습
____
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">import tensorflow as tf
# training data
x_data = [[1, 2, 1],
[1, 3, 2],
[1, 3, 4],
[1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5],
[1, 2, 5],
[1, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7]]
y_data = [[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0]]
# testing data - 학습이 끝난 후 학습된 모델 테스트하기 위해
x_test = [[2, 1, 1],
[3, 1, 2],
[3, 3, 4]]
y_test = [[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1]]
# 학습 데이터와 테스팅 데이터를 각각 입력할 수 있도록 placeholder 변수를 선언
X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 3])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 3])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3]))
hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X, W) + b)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(Y * tf.log(hypothesis), axis=1))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(cost)
prediction = tf.arg_max(hypothesis, 1)
is_correct = tf.equal(prediction, tf.arg_max(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initialize TensorFlow variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(201):
cost_val, W_val, _ = sess.run(
[cost, W, optimizer], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print(step, cost_val, W_val)
# predict
print("Prediction:", sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={X: x_test}))
# Calculate the accuracy
print("Accuracy: ", sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">실행결과
learning rate = 0.1
training set으로 학습 후 testing set으로 확인한 결과
올바른 예측 값과 100% 정확도를 보여준다.
200 6.68875 [[-0.99082351 0.0684003 -0.2845563 ]
[ 0.27955982 -0.91591495 0.28203434]
[ 0.45189726 0.28165713 1.49771595]]
Prediction: [2 2 2]
Accuracy: 1.0
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">실행결과
learning rate = 0.0000001
training set으로 학습 후 testing set으로 확인한 결과
cost 값(3.38216)이 일정하면서 변하지 않는것을 확인할 수 있다.
또한, 모델의 예측이 33%으로 정확도가 떨어졌다.
191 3.38216 [[ 0.77247852 0.66936469 -0.11435269]
[ 0.21988115 -1.46510637 0.28033131]
[ 0.91275501 0.5933395 0.64870787]]
192 3.38216 [[ 0.77247852 0.66936469 -0.11435269]
[ 0.21988115 -1.46510637 0.28033131]
[ 0.91275501 0.5933395 0.64870787]]
. . .
199 3.38216 [[ 0.77247852 0.66936469 -0.11435269]
[ 0.21988115 -1.46510637 0.28033131]
[ 0.91275501 0.5933395 0.64870787]]
200 3.38216 [[ 0.77247852 0.66936469 -0.11435269]
[ 0.21988115 -1.46510637 0.28033131]
[ 0.91275501 0.5933395 0.64870787]]
Prediction: [2 0 0]
Accuracy: 0.333333
</code></pre>
## 데이터 Normalization
____
- 데이터간의 값 차이가 크게 되면 Minimize를 위해 Normalization한다.
- 입력값을 학습한 결과가 inf, nan 등의 결과를 얻게되면 입력 데이터 셋이 잘못된 것이다.
- python numpy 라이브러리의 min(), max() 함수를 사용한 MinMaxScalar() 함수 정의해 Normalization을 해줄 수 있다.
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
xy = np.array([[828.659973, 833.450012, 908100, 828.349976, 831.659973],
[823.02002, 828.070007, 1828100, 821.655029, 828.070007],
[819.929993, 824.400024, 1438100, 818.97998, 824.159973],
[816, 820.958984, 1008100, 815.48999, 819.23999],
[819.359985, 823, 1188100, 818.469971, 818.97998],
[819, 823, 1198100, 816, 820.450012],
[811.700012, 815.25, 1098100, 809.780029, 813.669983],
[809.51001, 816.659973, 1398100, 804.539978, 809.559998]])
x_data = xy[:, 0:-1]
y_data = xy[:, [-1]]
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 4])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1])
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4, 1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
hypothesis = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-5)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(101):
cost_val, hy_val, _ = sess.run(
[cost, hypothesis, train], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print(step, "Cost: ", cost_val, "\nPrediction:\n", hy_val)
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px">실행결과
Non-Normalized 데이터 입력 결과
5 Cost: inf
Prediction:
[[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]
[-inf]]
6 Cost: nan
Prediction:
[[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]
[ nan]]
무한대와 nan 값이 발생해 학습이 제대로 이루어지지 않았다.
</code></pre>
<pre><code class="python" style="font-size:15px"># 정규화를 위한 MinMaxScaler() 정의
def MinMaxScaler(data):
numerator = data - np.min(data, 0)
denominator = np.max(data, 0) - np.min(data, 0)
# noise term prevents the zero division
return numerator / (denominator + 1e-7)
...
xy = MinMaxScaler(xy)
print(xy)
</code></pre>
> 소스코드 - 모두를 위한 머신러닝 김석훈 교수님 강의 참고 : ([https://hunkim.github.io/ml/](https://hunkim.github.io/ml/))
'Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TensorFlow - MNIST 데이터 셋 활용한 손 글씨 인식 모델 구현 (0) | 2017.08.07 |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow - Neural Network XOR 문제 (4) | 2017.08.03 |
| TensorFlow - Softmax Regression(2) (0) | 2017.07.13 |
| TensorFlow - Softmax Regression(1) (0) | 2017.07.12 |
| TensorFlow - Logistic Regression(로지스틱 회귀) (0) | 2017.07.09 |